Hemoglobin, is the main component of red blood cells. It is a mixture of protein known as globin and a compound known as heme that is made of iron and a pigment called porphyrin that gives the red color to our blood.
The important function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen to the organs and tissues from the lungs and carry carbon dioxide from organs and tissues back to the lungs. The levels of hemoglobin are measured using the hemoglobin test. Abnormalities in hemoglobin levels can indicate several conditions in the body.
Low levels of hemoglobin is called anemia which is characterized by a low red blood cell count and has different causes like vitamin deficiency, bleeding disorders, and chronic illnesses. Higher levels of hemoglobin can be due to smoking, dehydration, staying at higher altitudes, and blood disorders like polycythemia vera.
The Hemoglobin Test
The hemoglobin test is done as a part of the routine Complete Blood Count Test which identifies the count of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets inside the blood sample. The hemoglobin test is also performed during certain conditions including:
- Prior to or post-major surgery
- During pregnancy
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Throwing up blood in vomit or stools
- Issues related to bone marrow
- Chronic health issues
- Poor health conditions
- Monitoring certain medications
- Lack of nutrition
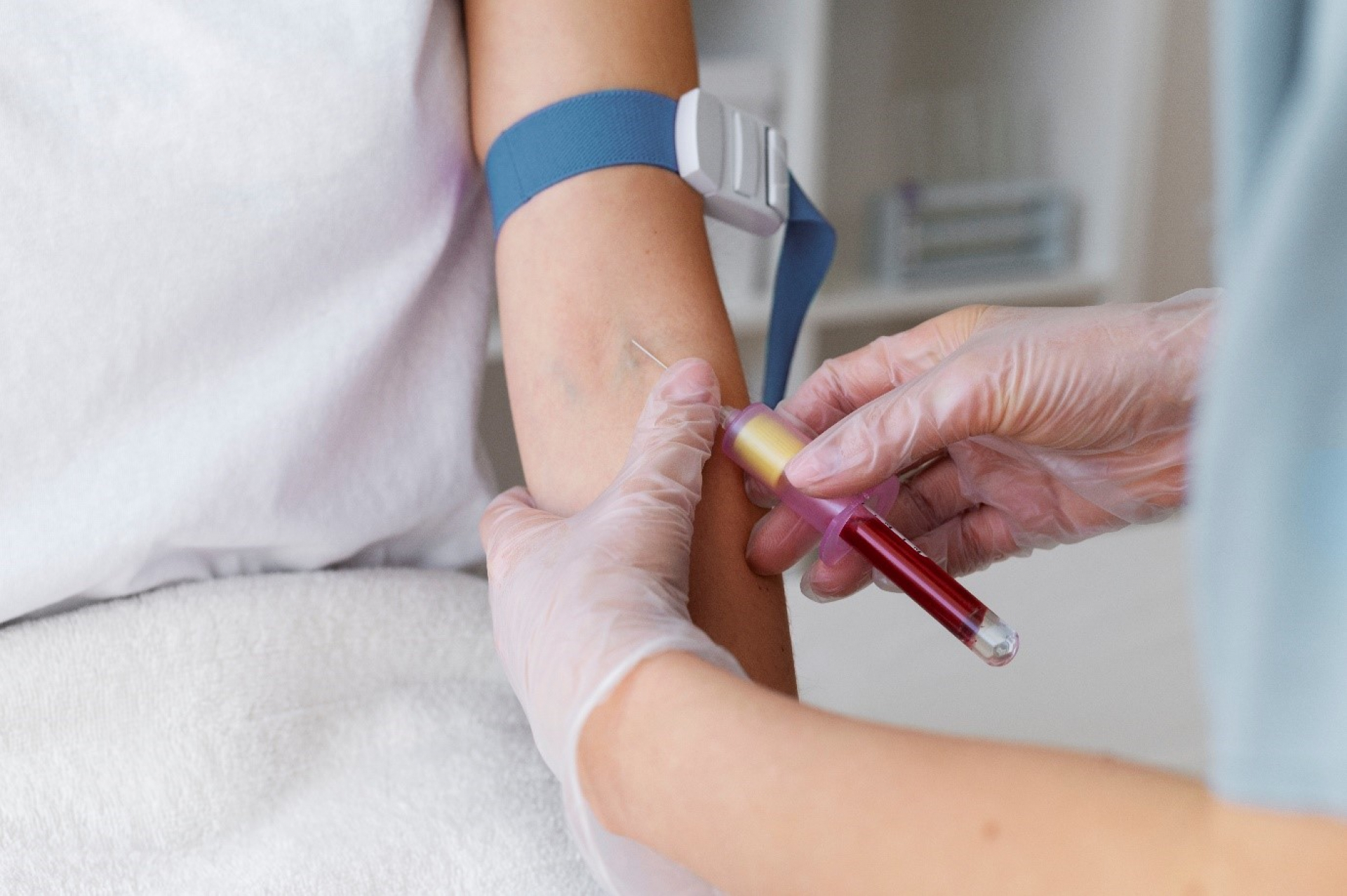
In any of the above-mentioned conditions, a sample of your blood is drawn from the vein of your arm and collected into a vial or test tube. No special preparation is required for the test. However, if your healthcare provider has ordered other tests along with the hemoglobin test fasting before the test might be recommended.
Very little risk is involved while drawing the blood sample. The size of the veins and arteries varies from person to person and from one side of the body to the other. But other risks include:
- Multiple pricking to find the veins
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or light-headedness
- Infection
- Blood clotting beneath the skin
Manifestations of Haemoglobin Abnormalities
A low hemoglobin level deprives oxygen from the tissues and organs, and the symptoms include:
- Weakness
- Tiredness
- Dizziness
- Dull skin
- Difficulty in breathing
- Frosty feet and hands
The high hemoglobin levels can thicken and make the blood dense peventing its free flow hence depriving the organs of oxygen. The common symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Itching
- Headaches
- Blurred or doubled vision
- Clots in the blood
Results
Manu conditions can alter the levels of your hemoglobin.
Lower levels of hemoglobin can be a sign of:
- Anemia
- Iron deficiency
- Liver disease
- Thalassemia
- Cancer and other illnesses
Higher levels of hemoglobin can be a sign of
- Heart disease
- Lung disease
- Polycythemia vera that causes fatigue, shortness of breath, and headaches
Interpretation of results
|
Normal results |
Range (g/dL) |
Range (g/L) |
|
Male |
13.8 to 17.2 |
138 to 172 |
|
Female |
12.1-15.1 |
121 to 151 |
|
Newborn |
14 to 24 |
140 to 240 |
|
Infant |
9.5 to 13 |
95 to 130 |
The range of the result may vary for adults and children based on the method used to measure the levels of hemoglobin. However, the above-mentioned range is the general range for the levels of hemoglobin in adults, infants, and newborns.
Based on the results your healthcare provider may discuss and order more tests. The treatment will depend on the condition because of which the level of hemoglobin is altered. The hemoglobin test is recommended regularly if undergoing treatment for blood disorders.
The hemoglobin test is a simple and easy process that helps in evaluating the knowledge about your health and it is a small part of the puzzle that explains how the blood cells function which maintain health. The alterations in the levels of hemoglobin can deprive the tissues and organs of oxygen. The levels of hemoglobin may vary in adults and children based on the method used and it is recommended to regularly undergo hemoglobin test for blood disorders.