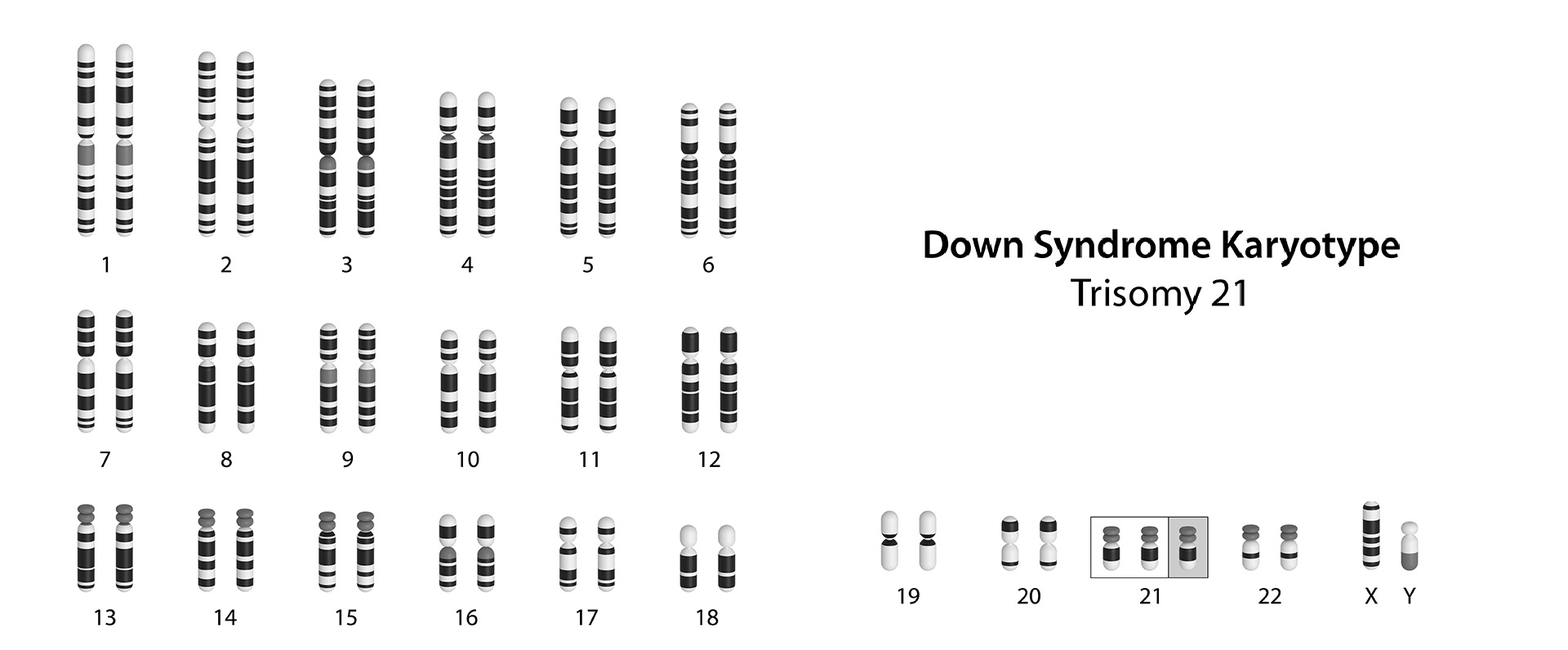
The human body is composed of billions of cells. Each cell consists of chromosomes (DNA-containing material) inside the nucleus of the cell. Aneuploidy is a hereditary (genetic) condition, where the number of chromosomes is less or more than 46. If there is the presence of an extra chromosome copy, it is called trisomy 47 or if there is a loss of one chromosome copy, it is called monosomy 45. Such conditions when present in the foetus, can lead to genetic abnormalities. Changes in the number of chromosomes can affect the pregnancy, most frequently leading to a miscarriage. With the increase in maternal age, the risk of foetal aneuploidy also increases.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a high throughput or massively parallel technology that determines the sequence of nucleotides (proteins) in the targeted regions of genomes (DNA or RNA). It provides accurate output, speed and scalability enabling new applications in clinical research, genomic, agricultural, forensic, environmental, and reproductive health. Miscarriages and unsuccessful implantations are primarily due to aneuploidy. Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) for aneuploidy can identify numerical and structural chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
Steps involved in next-generation sequencing
The four steps included in next-generation sequencing are nucleic acid isolation, library construction, clonal amplification and sequencing, and analysis of data.
Step 1- Nucleic Acid Extraction and Isolation:
It is an important step in next-generation sequencing. The method used for the extraction and isolation of nucleic acids will depend on the type of sample material (i.e. genomic DNA, or various types of RNA). The quality of isolated nucleic acids must be assessed before starting the next step.
Step 2- Library Construction:
It involves preparing samples of processed DNA or RNA by fragmenting them. The appropriate size of the target sample can be obtained by interacting with them on the NGS platform. Depending on the methods and reagents used, the library preparation may differ. The prepared NGS libraries contain fragments of DNA of the desired length.
Step 3- Clonal Amplification and Sequencing
It involves amplifying fragments of DNA by adding them to beads, ion surfaces, and flow cells. The sequencers will detect the strong fluorescent light. After this, the sequencer will be able to read the nucleotides one after one.
Step 4 -Data Analysis Using Bioinformatics
It involves stages such as processing, analysis, and interpretation of data, generated with the help of various bioinformatics tools. Depending on the goals and applications of NGS assay, the type of tool used may vary.
Types of next-generation sequencing
Next-Generation Sequencing is of three main types:
Whole Genome Sequencing
It is the sequencing of entire genetic material or DNA from an individual. It may include sequencing of both coding and non-coding DNA.
Whole Exome
It is the sequencing of the coding portions of DNA. An exome is a group of exons, which are DNA sequences, that must go through the processes of transcription and translation before being converted into proteins. Exome mutations are a major cause of genetic disorders. Therefore, WES is an efficient test for clinical diagnosis.
Targeted Panels or Gene Panel Sequencing
It is the sequencing that is performed on specific genes. It is efficient for the diagnosis of specific genetic disorders such as breast cancer and other cancers, skeletal and muscular disorders.
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) test
NIPT testing examines the fragments of free-floating DNA in a pregnant woman’s blood. These DNA fragments are called cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and they can be analysed to detect foetal abnormalities. Non-Invasive Prenatal Test can be done as early as the first 10 weeks of pregnancy. Healthcare providers recommend this test to determine whether a pregnant woman is at a higher risk of having a child who has a genetic disease.
NIPT test used for
NIPT is an effective method for screening for the following conditions:
- Congenital abnormalities
- Conditions affecting sex chromosomes (X and Y)
- Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
- Triple X syndrome (XXX)
- Jacob's Syndrome (XYY)
- Turner syndrome (Monosomy X/XO)
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Edward syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
It is also useful in identifying several chromosomal abnormalities such as sickle cell anaemia, thalassemia, and cystic fibrosis.
Types of NIPTs
Genesis Serenity
This test looks at the chromosomes that are present in the mother and foetus during pregnancy to determine the likelihood of genetic abnormalities.
Harmony
By analysing cell-free DNA in maternal blood, the harmony test identifies whether a newborn has a high or low risk of acquiring genetic disorders.
Panorama
A non-invasive prenatal screening test called Panorama can distinguish foetal DNA from maternal cell-free DNA. It screens for very rare chromosomal abnormalities.
NIPT test procedure
The NIPT test is usually carried out during the first trimester of pregnancy i.e. within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy. A simple blood sample is required for the NIPT test. Maternal blood is collected through a vein from the pregnant woman’s arm. The sample is then sent to the laboratory for testing for specific conditions.
Interpretation of the result:
- The NIPT detects the placental-derived foetal cfDNA in the mother's bloodstream. This is termed a foetal fraction. The foetal fraction must be greater than 4% to ensure the most accurate test findings.
- The NIPT test has the potential to identify a genetic disorder in the mother because it examines both maternal and foetal cfDNA.
- It takes around 2 weeks for NIPT test results.
- A positive result means the foetus may have a higher chance of a genetic disorder if the cfDNA level is higher than the normal range. To confirm any true-positive prenatal chromosomal abnormalities, positive results may require additional testing.
- A negative result implies that the foetus has a lower probability of developing genetic disorders to the non-functioning of chromosomes.
If you have a family history of genetic abnormalities, it is possible to have a healthy baby with an early diagnosis and proper treatment. Thus, getting prenatal aneuploidy screening through NGS and NIPT testing will predict the risk of a foetus having genetic disorders and provide information to the parents in advance to prepare themselves for a baby that may require special care.