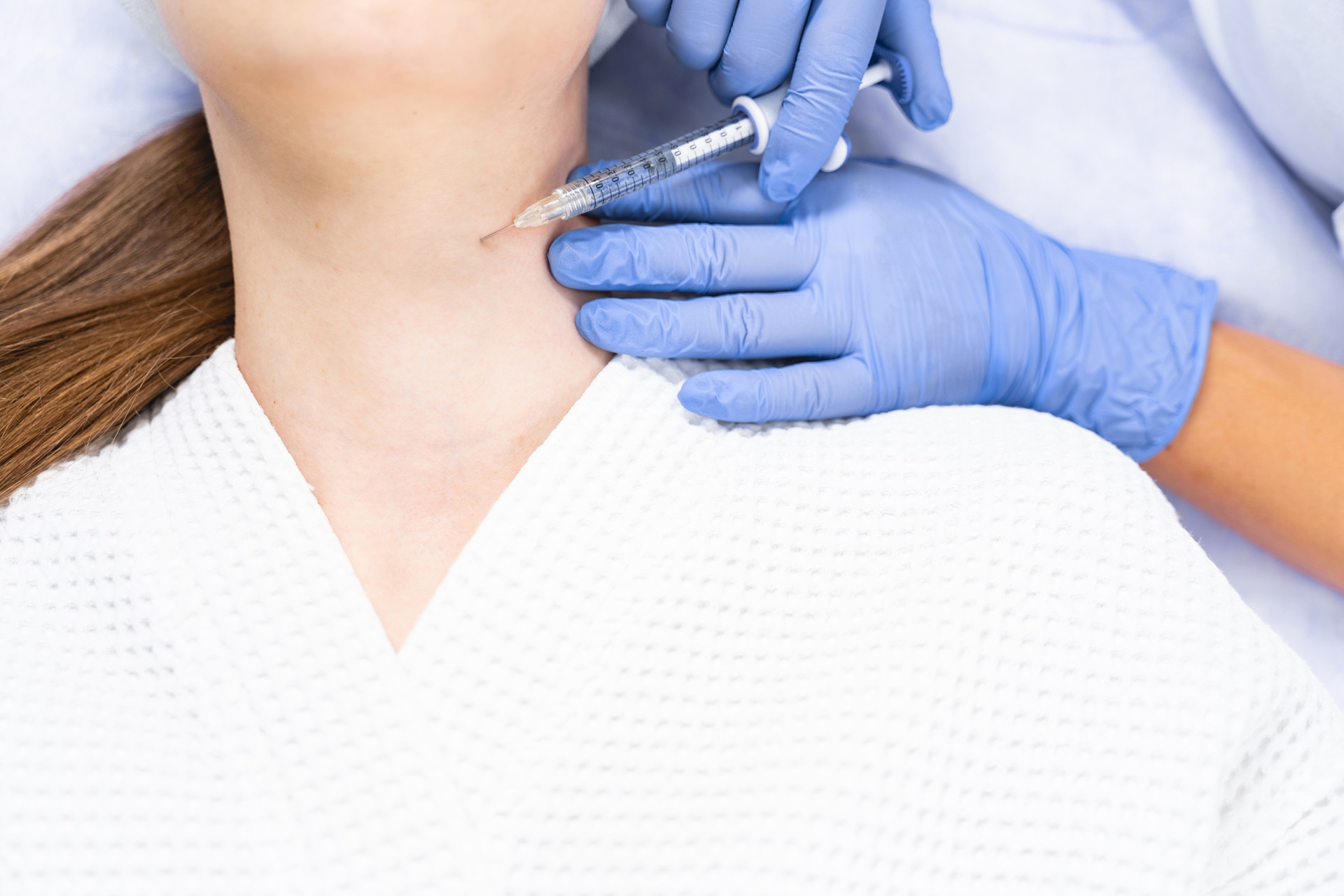
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), also known as aspiration biopsy, is a medical procedure performed on a suspicious lump or abnormal body area. It acts as a primary step to identify the cause of abnormal inflammation in the body and is usually performed on the breast or neck to detect disease conditions such as tuberculosis, lymphoma, etc. It involves collecting the sample cells from a region of the body using a fine-gauge needle and then sending them to the laboratory. It is a cost-effective, simple test often recommended by physicians to assess inflammatory diseases and other malignancies in the body.
Clinical Uses of FNAC:
FNAC is used to diagnose various disease conditions that involve lumps and masses. Some of the clinical uses of FNAC tests are
- It evaluates the presence of lumps in various organs and body parts, such as the armpit, skin, and groin.
- It helps in the early detection of head, neck, and breast cancer.
- It helps to detect the growth of tumors in the body.
- It diagnoses and differentiates benign and malignant tumors.
- It identifies cancer or the advancement of cancer from stages 1 to 4.
- It examines the risk of recurrence of cancer after radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery.
- It analyzes conditions that cause swelling, such as lymphomas, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, lymphomatous lymphoma, and granulomatous lymphadenitis.
- It helps check the fluid-filled cysts found during physical exams, x-rays, CTs, and MRIs.
- It helps physicians determine the efficacy of treatment.
The FNAC test for the neck is used to detect lumps and swollen nodes in the neck. In this test, a sample from the neck region is collected, which helps diagnose inflammatory and malignant conditions. It is mainly used to detect thyroid, salivary glands, lymph node disease, and neck masses.
Signs that indicate the need for an FNAC test
Physicians may suggest an FNAC test when they observe the following signs
- Lumps and masses on the body, such as on the breast, lymph nodes, thyroid, and other organs
- Changes in the size of a lump with skin changes, tenderness, and pain.
- Sudden onset of swelling or enlargement of glands or organs
- Abnormal findings in other tests, such as ultrasound and other imaging tests
- Inflammation and pus on the surface of the skin
Test Preparation
The FNAC test does not require any special precautions. Depending on the location of the lump or mass, the physician may provide additional advice. Wearing comfortable clothing is generally advised during the procedure; you may need to undress completely or partially, depending on the location of the lump. You should notify the physician regarding any supplements or medications you are taking. In certain situations, you may be advised to stop taking medications, like blood thinners.
Test Procedure
Fine needle aspiration is performed by cleaning the skin's surface with an antiseptic solution followed by draping the area with a sterile towel. Local anesthesia may be administered to minimize the pain and discomfort. Ultrasound is performed during the procedure to identify the location for needle aspiration, and then a thin needle connected to a syringe is inserted into the site. A vacuum is created inside the syringe, which results in the aspiration of bodily fluid or tissue into the syringe. The sample tissue is then sent to the laboratory; the entire process takes less than 10 minutes. Fine needle aspiration during endoscopy may require additional preparation. Patients may experience swelling, pain, or soreness after the procedure, and the physician may recommend over-the-counter medication to decrease the discomfort.
Benefits of FNAC
The FNAC offers several benefits, such as
- It is cheaper than other surgical procedures while also minimizing discomfort.
- It is cost-effective and gives rapid results.
- It has low-risk complications compared to surgical procedures.
- It assists in formulating a suitable treatment plan.
Interpretation of FNAC test results
The FNAC test results tell you whether the lump or nodule is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The size and location of the nodule, the site from which the sample is taken, and the skill of the practitioner conducting the test are some of the variables that affect the test's accuracy. The following are the results that may appear on your FNAC test report and their interpretations.
- Benign: The cells appear to be normal and non-malignant, which means the mass or lump is not cancerous.
- Suspicious: The cells appear to be abnormal, and they need further investigation to determine whether they are malignant or not.
- Malignant: The cells appear to be abnormal and possibly cancerous, and further testing is required to determine the severity and stage of cancer.
A positive FNAC test result means abnormal or malignant cells were found in the sample. A negative FNAC test result means the absence of harmful or abnormal cells in the test sample. It is important to discuss the test results with your healthcare provider.
The FNAC test is mainly used to determine the underlying cause of a lump or mass. This procedure helps identify the source of abnormal inflammation in the body and is usually carried out on the neck or breast to detect diseases such as tuberculosis, lymphoma, etc. Physicians recommend this simple and cost-effective test to evaluate lumps in the body, offering valuable insights into tissue abnormalities that aid in distinguishing between cancerous and noncancerous masses. Early detection is important for effective management of the disease condition. It is advised to seek medical attention when you find abnormal changes in the body.