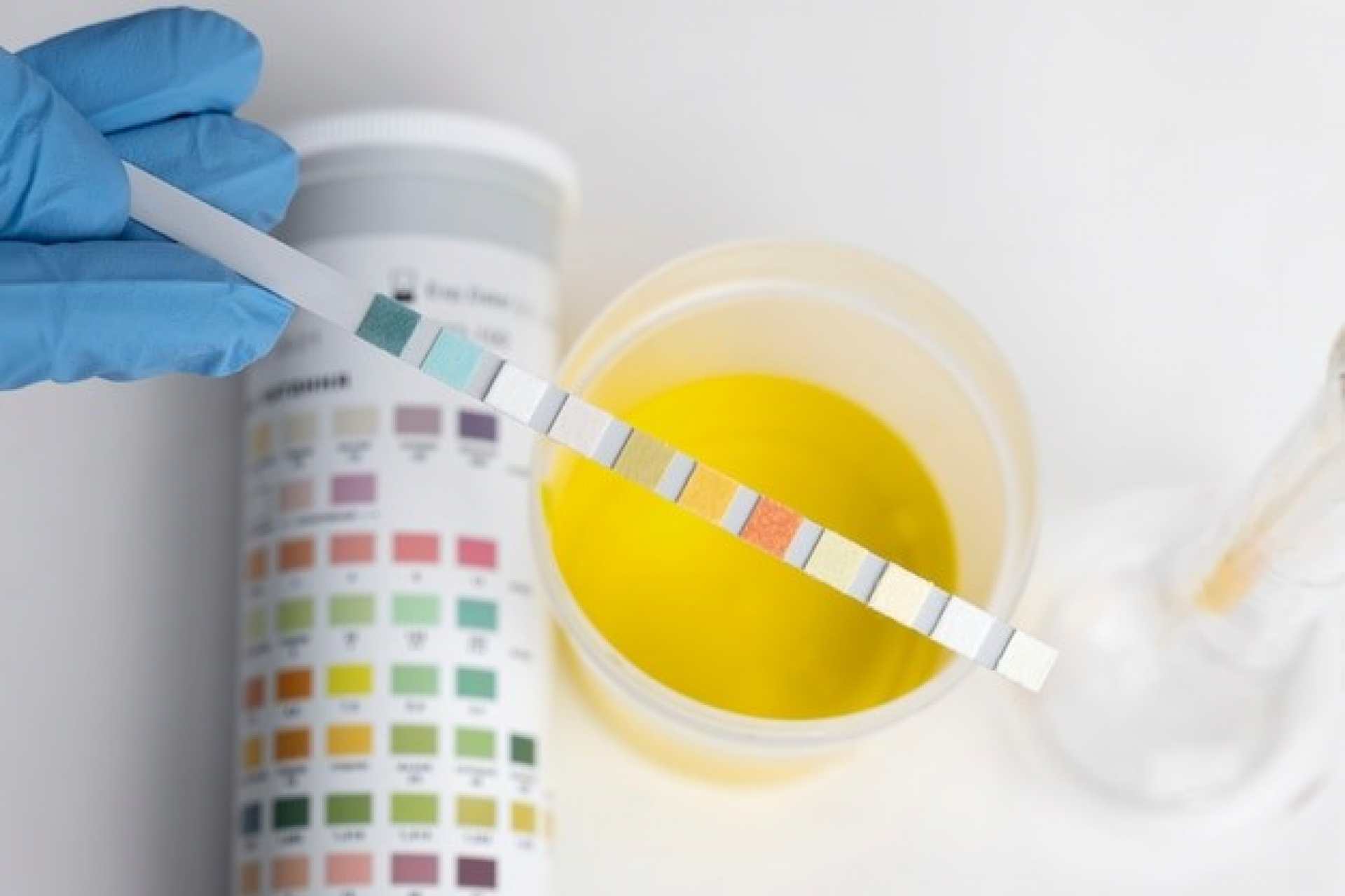
A urine test, also referred to as urine analysis or urinalysis, involves the examination of a sample of your urine by a healthcare provider to detect indications of kidney disease and other medical conditions. This test is utilized for the detection and management of a variety of disorders, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disease, and diabetes.
Purpose of urine tests
Urine tests help your healthcare provider:
- Assess your renal function
- Determine the particular stage of kidney disease
- Monitor health conditions that have the potential to lead to kidney disease, such as diabetes
- Check for potential issues arising from kidney disease, such as anemia and metabolic acidosis
- Check for additional issues like a kidney infection or a urinary tract infection (UTI)
The presence of protein in your urine can indicate kidney damage. Conducting a urine test enables the detection of kidney disease at an early stage before it progresses to a severe condition. Regular urine tests over time allow your healthcare provider to monitor the progression of kidney damage.
Symptoms of kidney damage
There
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Sleep problems
- Urinating more or less
- Swelling of feet and ankles
- Dry, itchy skin
- High blood pressure
The different types of urine tests
Healthcare providers employ a variety of tests to examine different things:
Visual exam: Healthcare providers examine the urine sample to observe its colour; dark yellow or brown urine may indicate an underlying issue. Also, they will check whether the urine is foamy, cloudy, or if there is any unusual odour, as these could be potential signs of a problem.
Microscopic exam: Healthcare providers examine a small quantity of urine through a microscope to detect indications of potential issues, including:
- Bacteria, which could indicate an infection
- Crystals, which may be indicative of kidney stones
- Red or white blood cells, which could be a sign of an infection or other kidney-related problems
Dipstick test: Healthcare providers use a thin plastic strip to test your urine, indicating levels of:
- Blood, potentially indicating issues like infection
- Protein, potentially indicating kidney disease
- Glucose (sugar), potentially indicating high diabetes levels
- Acidity (pH), abnormal levels of which may suggest problems like a UTI
Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR): Healthcare providers will conduct a urine test to measure the levels of albumin, the primary protein in your blood, and creatinine, a waste product from your muscles. If your UACR exceeds 30 mg/g, it might be indicative of kidney disease.
Microalbumin test: Healthcare providers may request this test to identify minimal protein levels in your urine if you have a health condition like diabetes or high blood pressure that increases your risk of kidney disease. If your albumin levels exceeds 30 mg/dL, it might be indicative of conditions such as urinary tract infections and kidney disease.
Urine culture: Healthcare providers order this test to diagnose kidney infection or urinary tract infection (UTI); a urine culture can reveal the specific type of bacteria present.
24-hour urine test: Healthcare providers assess the protein levels in urine samples collected over a span of 24 hours. This test may be requested if symptoms of glomerulonephritis or nephrotic syndrome are present. A 24-hour urine test may be advised for individuals with conditions such as
- Lupus
- High blood pressure
- Poorly managed diabetes
How is the sample collected for urine tests?
The urine is collected in different ways such as:
Clean catch: First wash your hands and clean your genitalia with a cleanser. Then begin urinating into a sterile cup provided by the doctor, which is then sent to the laboratory for analysis. This is the commonly used sample collection method in adults.
Urinary collection bag: This method is commonly used with children and infants. For this, a plastic bag is attached to the child’s genitalia with adhesive. When the child begins urinating, the bag catches the urine, which is then sent to a lab for analysis.
Catheter: Sometimes, a healthcare provider needs to collect a urine sample with a catheter. A sample of urine is taken by inserting a catheter, which is a thin rubber tube, through the urethra into the bladder. The urine is then drained into a sterile container and the catheter is removed.
Suprapubic aspiration: Rarely, a healthcare provider may need to collect a urine sample from the bladder with a needle. This procedure is known as a suprapubic aspiration, it is used if previous attempts of collecting an uncontaminated sample have been unsuccessful.
Treatment for a kidney infection
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for most kidney infections. Initially, healthcare providers commonly recommend an antibiotic that targets the prevalent types of kidney infections because immediate treatment is essential. Subsequently, they may adjust the antibiotic based on the results of blood or urine tests. In cases of severe infection, hospitalization for intravenous antibiotic administration may be necessary.
Prevention of kidney infections
It is possible to reduce the risk of developing a kidney infection by:
- Ensuring adequate hydration
- Emptying your bladder promptly when you feel the urge to urinate
- Urinating following sexual activity
- Practicing proper hygiene by wiping from front to back after using the restroom
- Avoiding the use of deodorant sprays in the genital area
Urine tests help to assess any abnormalities in the physical characteristics or chemical composition of your urine. This test is commonly utilized for the purpose of screening, diagnosing, and monitoring various health conditions, such as kidney disorders, diabetes, or UTIs. However, it is important to note that a urinalysis alone does not typically yield a conclusive diagnosis; further evaluation may be necessary if any unusual results are obtained. By analyzing the urine test findings alongside other diagnostic tests, your health care provider can determine the subsequent steps to be taken.
[sh1]Internal Link Added