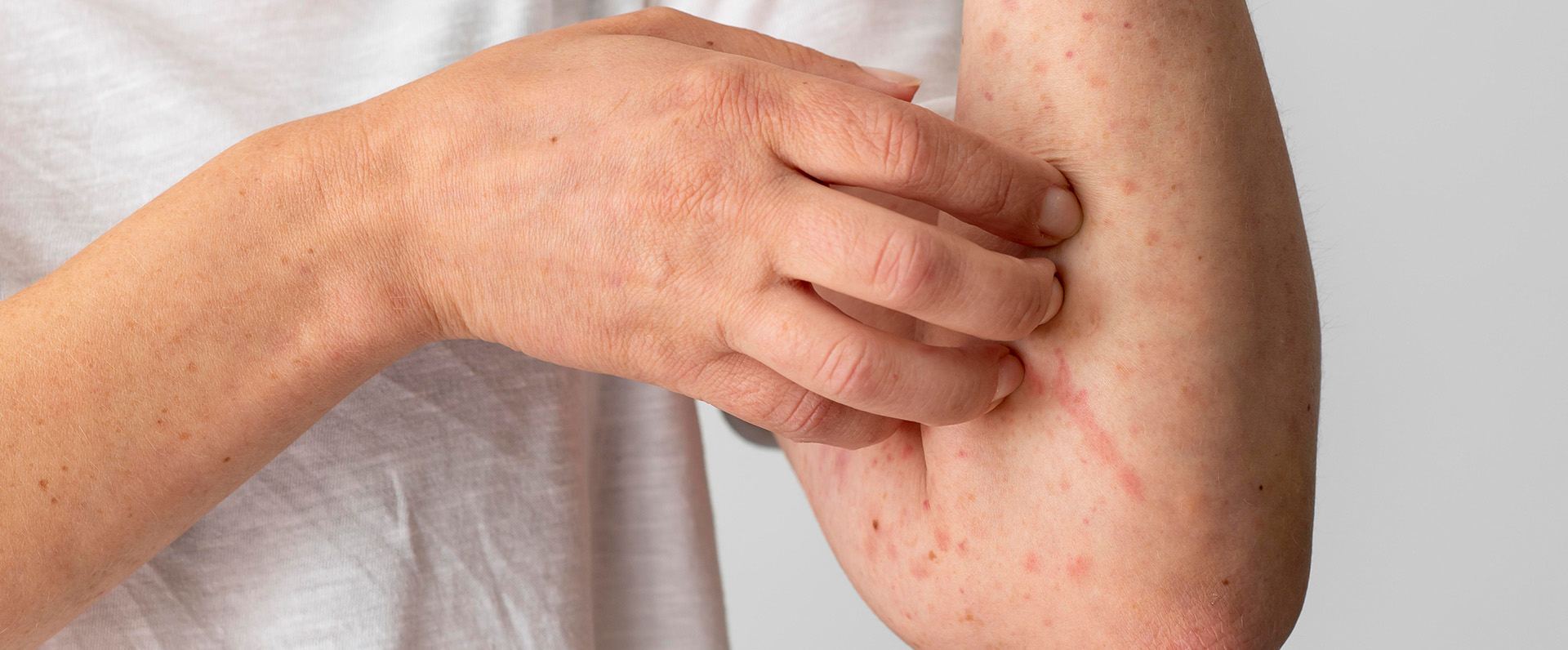
Every individual will suffer from one or another type of allergic reaction in the form of rashes during their lifetime. There are several types of rashes caused by toxins or illnesses such as chickenpox or roseola. If an individual develops an itchy rash when coming into contact with irritants, it could be due to allergic dermatitis.
Allergic dermatitis, or allergic contact dermatitis (CAD), is an inflammatory condition of the skin that is caused by a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. It occurs when a sensitized individual comes into contact with an offending chemical or allergen (e.g., poison ivy, certain fabrics, etc.) on the skin. Allergic contact dermatitis is common in the population with specific groups of employment such as health care workers, cleaners, metal workers, hairdressers, beauticians, and florists. Due to nickel and acrylate allergies, it is more common in women than men.
Causes of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis occurs due to exposure to a substance or allergen to which an individual is sensitive and triggers an immune reaction in the skin. It affects the areas that came into contact with the triggers (allergens).
Common allergens include:
- Nickel, a common metal used in jewellery, buckles, etc.
- Balsam of Peru, which is used in various products, such as perfumes, kinds of toothpaste, mouth rinses, and flavourings.
- Formaldehyde, a preservative used in cosmetics and other products.
- Personal care products, such as hair dyes and body washes.
- Plants, such as poison ivy and mango.
- Airborne allergens, such as insecticide spray and ragweed pollen.
- Certain creams, such as sunscreens and antibiotic creams.
Children can develop allergic contact dermatitis from common exposure to baby wipes, diapers, ear-piercing jewellery, clothing with snaps or dyes, etc.
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis
The signs and symptoms of allergic dermatitis can develop within minutes to hours of exposure to the allergen, and they can last up to 2 to 4 weeks.
Symptoms may vary widely and include:
- An itchy rash on the site of exposure
- Dry, scaly, cracked skin, typically on white skin
- Blisters and bumps, with oozing and crusting sometimes
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected area
- Leathery patches that are darker than usual (hyper-pigmented) on black skin
Diagnosis
It is easy to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis with proper medical and personal history, such as hobbies, work environment, sun exposure rate, and cosmetic products. The following are the various tests to be performed on patients with suspected contact allergies:
- Skin prick (scratch) test: A few droplets of potential allergens are dropped onto your skin and gently scratched, allowing these droplets to enter your skin. Within 10–15 minutes of exposure, reactions such as skin redness or a rash may occur. This test looks for allergies to airborne particles, foods, and penicillin.
- Intradermal skin test: This test is recommended if your skin prick test results were negative or inconclusive. In this test, your epidermis (outer layer of the skin) is exposed to trace amounts of allergens. This test looks for allergies to irritants in the air, medications, and insect stings.
- Patch test: This test aids in the diagnosis of contact dermatitis, particularly if the reaction is severe, recurrent, or chronic. You may be given an allergen-containing patch (bandage). You are to leave the bandage on for 48–96 hours. If you notice any rash or reactions after removing the bandage, it is likely the reason for your contact dermatitis.
- Blood test (IgE): Your blood sample is taken, and allergens are added to it. The levels of IgE antibodies are measured after the allergens are added to the blood sample. These tests could produce false-positive results at times.
- Challenge test: This test is performed under the supervision of a medical professional. It entails administering a suspected allergen or drug that is suspected of causing an allergy. If you have an abnormal reaction to this, an epinephrine injection is given right away to stop the reaction.
- Open application test: It is performed to determine if there is an allergy due to a cosmetic product such as a moisturizer. In this test, the suspected product is applied several times a day over a small area of sensitive skin. If you notice any rashes, that is likely the reason for your dermatitis.
- Others: Fungal scrapings of the skin and a Dimethylgloxime test can be performed to identify nickel allergies.
Interpretation of the results:
Positive test result
If the test results are positive on the allergy panel, it means you are allergic to that particular allergen. Even if you are allergic to certain allergens, it is not always necessary that you will have a reaction to them. Sometimes the results may also show false positives, especially from a blood test. A false-positive result indicates you have an allergy to certain allergens even though you don’t.
Negative test result
If the test results are negative on the allergy panel, it means you are not allergic to that particular allergen.
The best way to prevent and manage contact dermatitis is to avoid offending substances or allergens, choose moisturizers and cleansers that are free of fragrance, and wash skin and hands regularly after exposure to any allergens or irritants. Owing to genetic and environmental factors, allergic dermatitis is a common skin allergy. Hence, it is advised to get tested for allergic dermatitis in order to avoid possible anaphylactic reactions.