Non-invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
About NIPT test
NIPT test is also called non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS). This testing examines small fragments of free-floating DNA in a pregnant woman’s blood. These DNA fragments are called cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and they can be analysed to detect fetal abnormalities. This test is used by medical professionals to determine whether a pregnant woman is at a higher risk of having a child who has a genetic disease.
Types of NIPTs
Genesis Serenity
This test looks at the chromosomes that are present in the mother and foetus during pregnancy to determine the likelihood of abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edward's syndrome, and Patau syndrome.
Harmony
By analysing cell-free DNA in maternal blood, the Harmony test identifies whether a newborn has a high or low risk of acquiring trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), or trisomy 13. (Patau syndrome)
Panoramo
A non-invasive prenatal screening test called Panorama can distinguish foetal DNA from maternal cell-free DNA. Panorama checks the baby's gender and some of the most prevalent genetic disorders. It screens for very rare chromosomal abnormalities.
What is a NIPT test used for?
NIPT is an effective method for screening the following conditions:

Congenital abnormalities

Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)

Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)

Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)

Disorders affecting sex chromosomes (X and Y)

Turner syndrome (Monosomy X/XO)
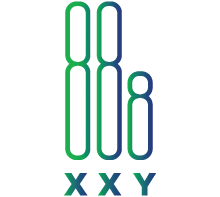
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
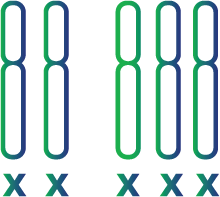
Triple X syndrome (XXX)
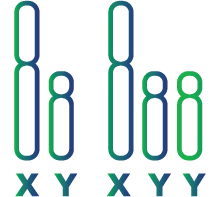
Jacob’s Syndrome (XYY)

sickle cell anaemia

Thalassemia
Cystic fibrosis
Who should get tested?
NIPT test is recommended for pregnant women who are at high risk of having an abnormal child. The following factors can increase the risk:

Advanced maternal age (>35 years)

History of infertility
History of stillbirths

Nutritional deficiencies (e.g. Iron)
Diabetes

Hypothyroidism
Infections (e.g. rubella, syphilis)
Test Preparation
Non-invasive prenatal testing is done to establish whether the unborn child has any congenital abnormalities. Special preparation and fasting are not required to perform this test. The NIPT test is usually carried out during the first trimester of pregnancy i.e. within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy. A simple blood sample is required for conducting the NIPT test. Maternal blood is collected through a vein from the pregnant woman’s arm. The sample is then sent to the laboratory for testing for specific conditions
Types of NIPT techniques
NIPT and Whole-Genome Sequencing
It provides the most effective and accurate results of NIPT, which offers a thorough overview of the complete genome.
Targeted Approaches for NIPT
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, microarray analysis, and rolling circle amplification are some of the targeted technologies for NIPT. With targeted methods, only a small portion of chosen chromosomes are examined.
Interpretation of the result:
· The NIPT detects the placental-derived foetal cfDNA in the mother's bloodstream. This is termed a foetal fraction. The foetal fraction must be greater than 4% to ensure the most precise test findings. This typically occurs during the 10th week of pregnancy, and hence this test is recommended then.
· The NIPT test has the potential to identify a genetic disorder in the mother because it examines both maternal and foetal cfDNA.
· It takes around 2 weeks to get the result of the NIPT test.
· A “Negative” result implies that the foetus has a lower probability of developing genetic disorders to the non-functioning of chromosomes.
· A “positive” result means the foetus may have a higher chance of a genetic disorder if the cfDNA level is higher than the normal range. To confirm any true-positive prenatal chromosomal abnormalities, positive results may require additional testing.
FAQs
Why is the NIPT test necessary?
NIPT test helps in identifying a foetus at risk of chromosomal abnormalities. It provides comfort to expectant parents, gives early information that improves the management of a child's genetic health wherever possible, and prepares for childbirth and early intervention
I am an 8-week pregnant woman. Can I opt for a NIPT test at this stage?
NIPT analyses cell-free DNA or cfDNA fragments that circulate in the maternal bloodstream about 10 weeks into the pregnancy. Thus, you should opt for a NIPT test only after 10 weeks
Is there any risk to the NIPT test?
NIPT test is a completely safe and effective way of detecting fetal abnormalities and does not involve any risk
What other tests are needed as a follow-up if the NIPT test indicates that the fetus is at risk of some congenital disorder?
If the NIPT test indicates some risk to the fetus, it can be confirmed through diagnostic tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
Is it recommended for all pregnant women to undergo the NIPT test?
Undergoing a NIPT test during pregnancy is not mandatory. It is a personal choice that can be taken after a discussion with your healthcare provider
Does the NIPT test indicate the sex of the fetus?
Yes, the NIPT test can indicate the sex of the fetus